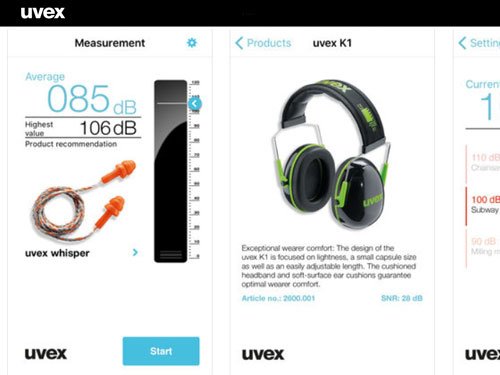
Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) and its impact
The World Health Organisation states "Noise induced hearing loss is the most common, permanent and irreversible injury in the world and tinnitus is the third most serious non-fatal medical condition".
In Australia, between July 2002 and June 2007, there were approximately 16,500 occupational NIHL workers compensation claims In addition to the financial costs associated with noise-induces hearing loss, there are wider implications of hearing loss to the individual, their quality of life and the impact it can have on their family.

What is noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL)?
Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is the sudden or gradual loss of hearing due to exposure to loud sounds.
Loud noises can damage the hair cells in the inner ear and the hearing nerve. Hair cells are not replaceable and do not regrow. Damaged hair cells are unable to trigger electrical signals to the brain, impeding hearing. Prolonged exposure to excessive levels of noise (such as industrial machinery, heavy traffic or even loud music) can cause noise-induced hearing loss. One-time exposure to extremely loud sounds such as explosions or gunshots can cause immediate and irreversible hearing loss.
These loud sounds cause damage to the ear structures and delicate hair cells, which play a vital role in transmitting sound waves to the brain. The most common symptom of noise-induced hearing loss is a gradual onset of high-frequency hearing loss. The progressive nature of the damage - and the fact that it does not hurt - means many people do not notice anything is wrong until it is already quite severe.
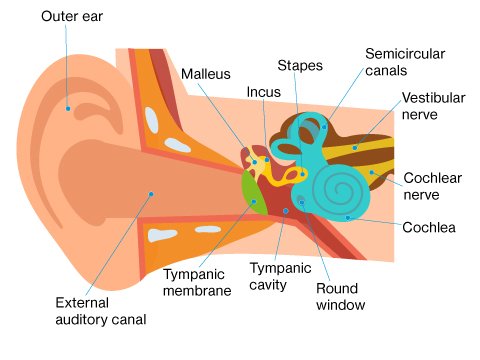
What are the symptoms of noise-induced hearing loss?
Having trouble hearing is the main symptom of noise-induced hearing loss. If you have any of these signs or symptoms, you may have hearing loss caused by noise:
- Trouble hearing soft or faint sounds
- Normal conversation and other sounds may sound muffled or unclear
- Ringing or buzzing in the ears (Tinnitus)
- Difficulty hearing high-pitched sounds (e.g. doorbell, telephone, alarm)
- Hypersensitivity to certain sounds
The wider implications of hearing loss
Noise induced hearing loss leads to communication problems. Relationships with family, friends and work colleagues may also suffer. Noise induced hearing loss may result in not being able to hear warning sounds (such as alarms) or workplace noises such as supervisors giving directions and could result in increased absenteeism and lower productivity.

Socio
- Impact on family life
- Impact on life quality and lifestyle
- Risk of alienation
- Speech deterioration

Economic
- Potential loss of income
- Reduced productivity
- Cost to the employer in individual hearing aids

Risks
- Failure to hear alarms = danger
- Failure to hear instructions = frustration

Hearing loss is not inevitable
The risk of noise-induced hearing loss can be significantly reduced through the proper selection and use of hearing protection. Contrary to popular belief, hearing loss is not inevitable - it can be prevented by identifying the exposure levels, reducing the risk of harmful noise levels at source, or by wearing adequate and suitable hearing protection which has been correctly fitted.
How to fit disposable earplugs?
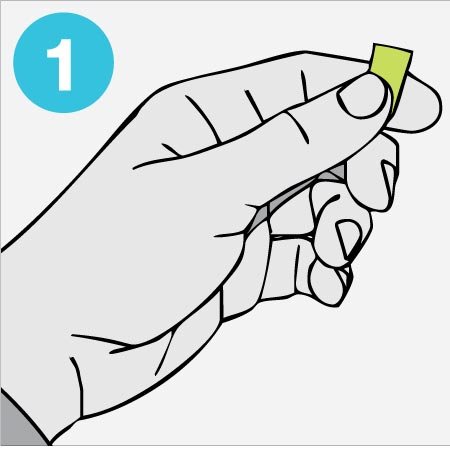
Roll down uvex disposable hearing protection plugs.
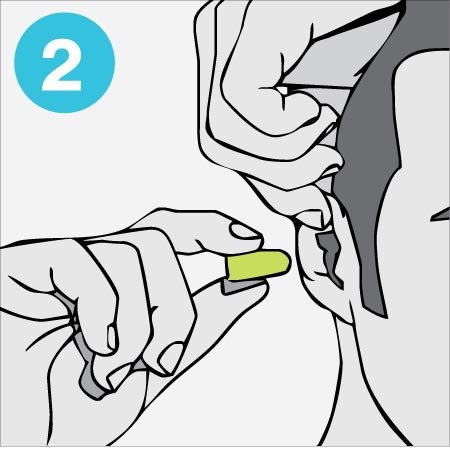
Put your arm over your head and move the ear slightly upwards to straighten your auditory canal. This achieves a better fit.
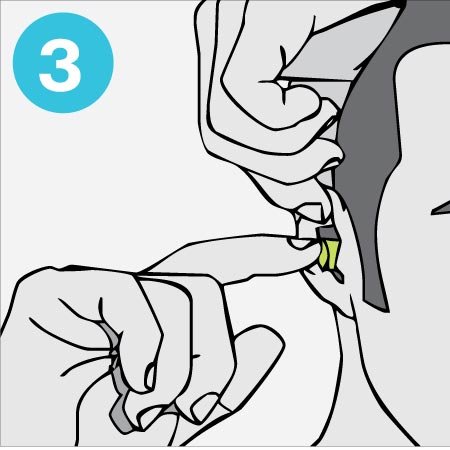
Insert plugs and hold in place while they expand. If they are not visible from the front, then they are in the right position.
uvex Product Trial Program
Our goal is to work with you together to help reduce injuries and lower your PPE costs. We surround our products with an array of services which support PPE decision makers in selection and safety strategy implementation ensuring that PPE wearers derive maximum benefit in terms of protection and ‘issue free’ wearability.
FIND OUT MORE